What is vulnerability management?
In this blog, we discuss what vulnerability management is, the lifecycle from discovering weaknesses to prioritising, resolving, and continuously improving defences to minimise cyber risks.

Manoj Korekka
7th October 2024
Today’s digital world exposes organisations to increasing cyber threats. As technology advances, so do the tactics of threat actors. Vulnerability management is key to protecting systems and strengthening cybersecurity.
Understanding the fundamentals
Vulnerability management is the ongoing, regular process of identifying, assessing, reporting on, managing and remediating cyber vulnerabilities across endpoints, workloads and systems. At its core, it’s about staying one step ahead of potential threats by proactively addressing weaknesses before they can be exploited.
A strong vulnerability management programme leverages threat intelligence and a deep understanding of IT and business operations to prioritise risks effectively. By doing so, organisations can address vulnerabilities as quickly as possible, minimising their exposure to potential attacks.
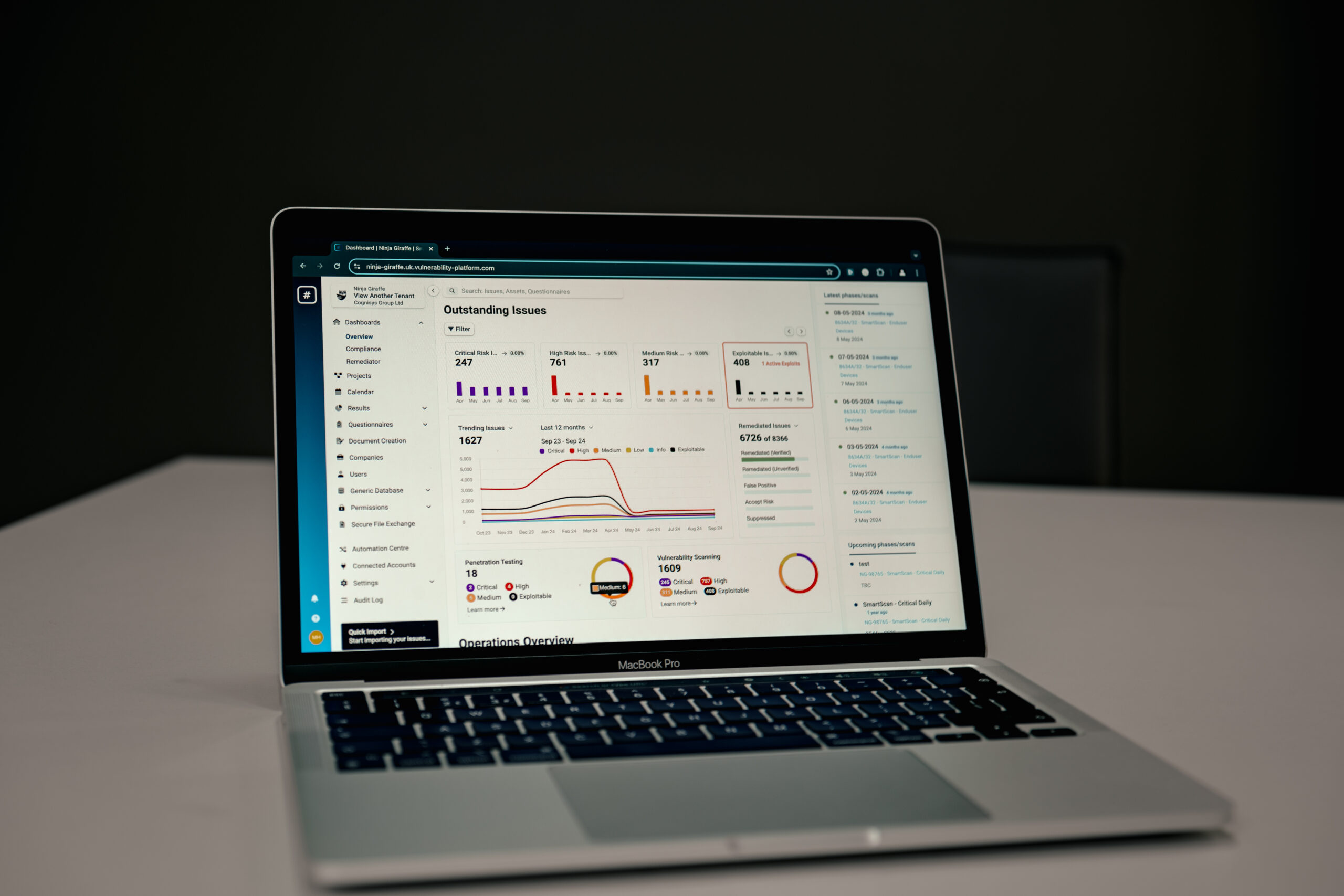
The vulnerability management workflow
The vulnerability management process isn’t a one-time event but a continuous cycle consisting of several key stages:
1. Discovery
This initial stage involves identifying vulnerabilities through various assessment methods. Organisations typically employ vulnerability scanners to systematically probe their networks, systems, and applications. Regular penetration testing is also crucial, as it simulates real-world attack scenarios, uncovering vulnerabilities that automated scans might miss.
2. Categorisation and Prioritisation
Once vulnerabilities are identified, they need to be classified and prioritised. This stage often utilises frameworks like the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) to assess severity. However, effective prioritisation goes beyond just CVSS scores – it considers factors such as the criticality of affected assets, the potential business impact, and the current threat landscape.
3. Resolution
Remediation can take various forms, including applying security patches, updating software, or implementing other mitigation techniques. In some cases, when immediate patching isn’t feasible, organisations might need to employ compensating controls to mitigate risk.
4. Reassessment
After remediation efforts, it’s crucial to verify that vulnerabilities have been successfully resolved. This typically involves re-scanning systems and conducting follow-up penetration tests to ensure that the applied fixes are effective and haven’t introduced new vulnerabilities.
5. Reporting
The final stage involves documenting and reporting on the entire vulnerability management process. This helps track trends over time, ensures compliance with regulatory requirements, and provides valuable insights for improving the overall security posture.

Key concepts: Vulnerability, risk, and threat
Vulnerability
This is a weakness in an asset or group of assets that can be exploited by one or more threats. Vulnerabilities can exist in various forms, such as software bugs, misconfigurations, or design flaws.
Threat
A threat is any entity or circumstance that can exploit a vulnerability. Threats can be external (like cyber criminals or nation-state actors) or internal (such as disgruntled employees).
Risk
Risk represents the potential damage or loss that could occur when a threat exploits a vulnerability. It’s typically measured in terms of likelihood and impact.
Understanding the interplay between these concepts is crucial for effective vulnerability management. By identifying vulnerabilities, assessing potential threats, and evaluating risks, organisations can make informed decisions about where to focus their security efforts.
Vulnerability severity rankings
The Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) is a free and open industry standard used to assess and communicate the severity of software vulnerabilities. The CVSS Base Score ranges from 0.0 to 10.0, with the following severity ratings:
0.1-3.9: Low
4.0-6.9: Medium
7.0-8.9: High
9.0-10.0: Critical

Choosing the right vulnerability management solution
With the increasing complexity of IT environments, selecting an appropriate vulnerability management solution is crucial. When evaluating options, consider the following factors:
Timeliness
The tool should detect vulnerabilities quickly and provide up-to-date information. In the fast-paced world of cyber security, outdated information can be almost as dangerous as no information at all.
Performance impact
Look for a solution with a lightweight agent to minimise impact on endpoint performance. The last thing you want is for your security measures to significantly slow down your systems.
Visibility
Seek real-time, comprehensive visibility into your organisation’s risk posture. This includes coverage across all assets – from on-premises systems to cloud environments and IoT devices.
Integration
The solution should integrate well with other security tools and processes. This enables a more holistic approach to security and can streamline remediation efforts.
Automation
Consider tools that use automation and machine learning to prioritise and remediate vulnerabilities efficiently. As the volume of vulnerabilities continues to grow, automation becomes increasingly important for managing them effectively.
Recent vulnerability management trends and statistics
The landscape of vulnerability management is constantly evolving. Here are some recent trends and statistics that highlight its importance:
- By 2025, it’s predicted that 45% of global organisations will be impacted by supply chain attacks, emphasising the need for robust security measures across interconnected networks.
- The number of reported vulnerabilities is expected to grow significantly, with projections indicating a 25% increase from 2023 to 2024, necessitating proactive vulnerability management strategies.
- Over 29,000 Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVEs) were published globally in 2023, marking a 15% increase from the previous year. This trend is expected to continue, with projections indicating a 25% increase from 2023 to 2024.
- Cyber crime is projected to cost the world approximately $9.5 trillion in 2024, with expectations to rise to $10.5 trillion by 2025, reflecting a growing trend in cyber threats and attacks.

Best practices for effective vulnerability management
To maximise the effectiveness of your vulnerability management efforts, consider the following best practices:
Adopt a risk-based approach
Not all vulnerabilities are created equal. Prioritise based on the potential impact to your organisation, considering factors like asset criticality and exploitability.
Implement continuous monitoring
The threat landscape is constantly changing. Implement tools and processes for continuous vulnerability scanning and assessment.
Foster collaboration
Effective vulnerability management requires cooperation between security teams, IT operations, and business units. Establish clear communication channels and shared objectives.
Automate where possible
Use automation to streamline routine tasks like vulnerability scanning and patch management. This frees up your security team to focus on more complex issues.
Stay informed
Keep abreast of the latest vulnerabilities and threats. Leverage threat intelligence feeds and participate in information-sharing communities.
Regularly test your defences
Don’t rely solely on automated scans. Conduct regular penetration tests to identify vulnerabilities that automated tools might miss.
Document and learn
Maintain detailed records of your vulnerability management activities. Use this information to identify trends and continuously improve your processes.
As the threat landscape continues to evolve, vulnerability management remains a critical priority for organisations of all sizes. By adopting a proactive, risk-based approach and leveraging the latest tools and best practices, organisations can better protect themselves against cyber threats and minimise the impact of potential breaches.
Remember, vulnerability management is not a one-time effort but an ongoing process. It requires dedication, resources, and a commitment to continuous improvement. However, the investment pays off in enhanced security, reduced risk, and greater peace of mind in an increasingly digital world.
By making vulnerability management a cornerstone of your cyber security strategy, you’re not just defending against today’s threats – you’re building resilience against the challenges of tomorrow.
If you want an ally in vulnerability management capable of delivering all the essentials we’ve listed and more, a service that watches over your IT estate 24/7, then learn more about SmartScan service.