Key features your vulnerability management platform must have
In this blog, we delve into the core concepts of vulnerabilities and the significance of a robust vulnerability management platform.

Manoj Korekka
19th June 2024
This blog aims to provide an in-depth exploration of vulnerability management, a critical aspect of cyber security that involves identifying, analysing, prioritising, and addressing weaknesses or flaws within an organisation’s IT infrastructure.
It’s vitally important to have a vulnerability management platform with key features like asset inventory, vulnerability scanning, patch management, risk prioritisation, and continuous monitoring.
Understanding vulnerabilities
A vulnerability is a weakness or flaw in a system, application, or network that can be exploited by cyber criminals to gain unauthorised access, disrupt operations, or compromise sensitive data. Vulnerabilities can arise from various sources, including software bugs, misconfigurations, outdated systems, or human errors.
These vulnerabilities pose significant risks to organisations, as they can be leveraged by threat actors to launch attacks, such as data breaches, distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks, or ransomware infections.
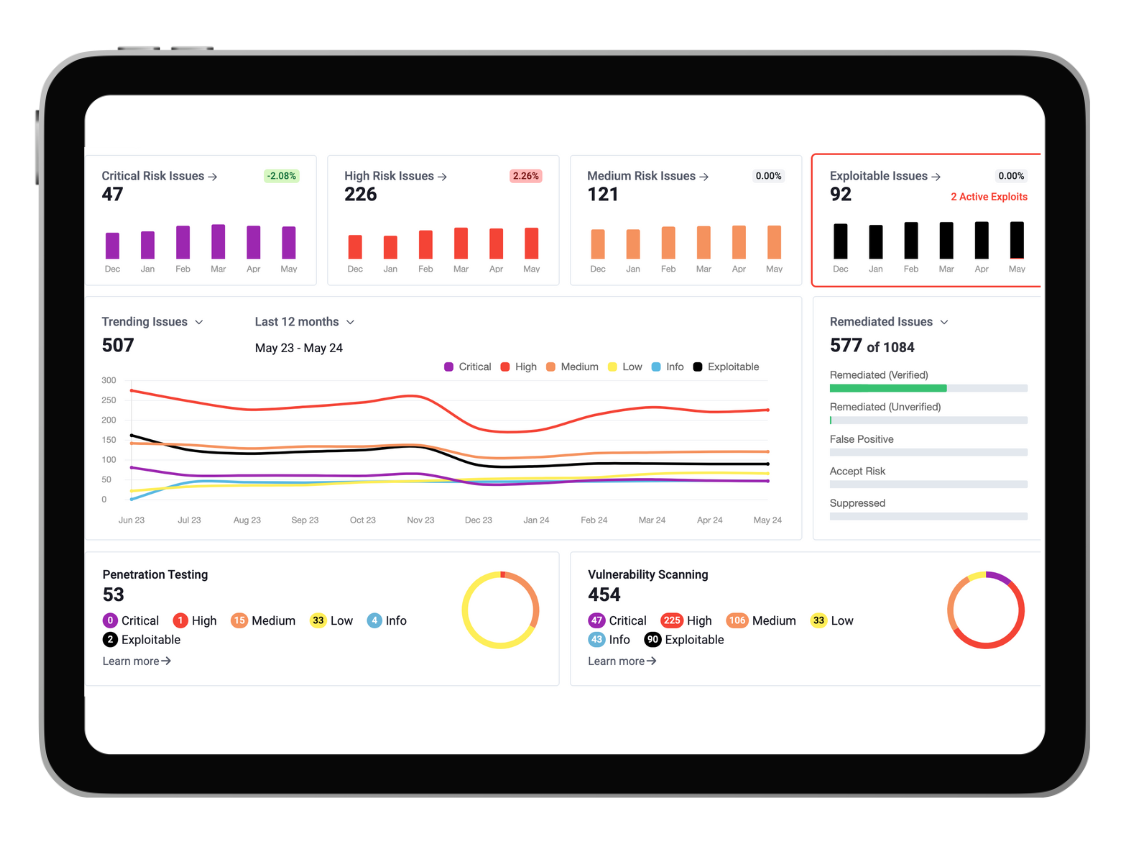
See an example of our vulnerability management service, SmartScan, where the dashboard showcases the number of vulnerabilities categorised into critical, high, medium, and exploitable ratings.
The benefits of effective vulnerability management
Vulnerability management is a systematic approach to identifying, analysing, prioritising, and addressing vulnerabilities within an organisation’s IT infrastructure. By implementing an effective vulnerability management program, organisations can proactively identify and remediate vulnerabilities before they are exploited, reducing the risk of cyber-attacks and data breaches.
Risk mitigation
By identifying and addressing vulnerabilities promptly, organisations can reduce the potential impact of cyber threats and minimise the risk of data breaches, system downtime, and reputational damage.
Compliance
Many regulatory bodies and industry standards, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), and ISO 27001, mandate vulnerability management practices. Implementing a robust vulnerability management program helps organisations comply with these regulations and avoid costly penalties.
Operational efficiency
By proactively addressing vulnerabilities, organisations can minimise the need for reactive measures, such as incident response and recovery efforts, which can be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
Improved security posture
A comprehensive vulnerability management program provides organisations with a better understanding of their attack surface, enabling them to prioritise remediation efforts and allocate resources more effectively.

Essential tools for vulnerability management
Any effective vulnerability management platform should have these key features:
Asset inventory and discovery
Maintain an accurate and up-to-date inventory of all IT assets, including hardware, software, and network components. This enables organisations to identify and prioritise vulnerabilities based on the criticality of the affected assets.
Vulnerability scanning and assessment
Regularly scan and assess systems, applications, and networks for vulnerabilities. This can be achieved through automated vulnerability scanning tools, penetration testing, and manual assessments. Prioritise vulnerabilities based on their severity and potential impact.
Patch management
Implement a robust patch management process to ensure that systems and applications are promptly updated with the latest security patches and updates. This helps mitigate known vulnerabilities and reduces the risk of exploitation.
Configuration management
Maintain secure configurations for all systems, applications, and network devices. Regularly review and update configurations to align with industry best practices and vendor recommendations.
Risk prioritisation and remediation
Establish a risk-based approach to prioritise and remediate vulnerabilities. Consider factors such as the severity of the vulnerability, the criticality of the affected asset, and the potential impact on the organisation’s operations and reputation.
Continuous monitoring
Implement continuous monitoring processes to detect and respond to new vulnerabilities and changes in the IT environment. This includes monitoring security advisories, threat intelligence feeds, and industry best practices.
Vendor and third-Party management
Implement continuous monitoring processes to detect and respond to new vulnerabilities and changes in the IT environment. This includes monitoring security advisories, threat intelligence feeds, and industry best practices.
Training and awareness
Educate employees on the importance of vulnerability management and their role in identifying and reporting potential vulnerabilities. Provide regular security awareness training to promote a culture of security within the organisation.
Incident response and recovery
Develop and maintain an incident response plan to address and recover from security incidents that may occur due to unmitigated vulnerabilities. This includes procedures for containment, investigation, and remediation.
Continuous improvement
Regularly review and assess the effectiveness of the vulnerability management program. Identify areas for improvement and implement necessary changes to enhance the program’s effectiveness and align with evolving security best practices.
Find the right vulnerability management platform for your business
Vulnerability management is a critical component of an organisation’s cyber security strategy. By adopting a proactive approach and implementing effective vulnerability management practices, organisations can significantly reduce their exposure to cyber threats, mitigate risks, and enhance their overall security posture.
Organisations must prioritise vulnerability management and allocate the necessary resources to ensure a robust and effective program is in place. By taking proactive measures, organisations can stay ahead of emerging threats and protect their valuable assets, data, and reputation.
If you want an ally in vulnerability management capable of delivering all the essentials we’ve listed and more, a service that watches over your IT estate 24/7, then learn more about SmartScan here.