Cyber Essentials Control Changes for 2023
The Cyber Essentials requirements have been updated to include several changes. Firstly, the definition of ‘software’ has been updated to clarify that firewall and router firmware is included in the scope.
Additionally, asset management is emphasised as an important security function, with the Cyber Essentials requirements recommending establishing and maintaining accurate information about assets.
The NCSC’s guidance on BYOD has been added for further information, and a table has been included to clarify which third-party devices are in scope for the assessment. The ‘device unlocking’ section has been updated to reflect vendor restrictions, and the ‘malware protection’ section has been updated with the latest research and vendor recommendations.
Finally, information has been added on how using a zero-trust architecture affects Cyber Essentials. These changes aim to provide greater clarity and relevance to current cybersecurity threats and practices.
This year, the changes to the scheme are as follows:
1. The definition of ‘software’ has been updated to clarify where firmware is in scope
Software includes operating systems, commercial off-the-shelf applications, plugins, interpreters, scripts, libraries, network software and firewall and router firmware.
Why the change?
Firewall and router firmware is the operating system of those devices. As firewalls and routers are key security devices, their operating systems and whether they are kept up to date is extremely important from a security perspective.
And another thing…
Cyber Essentials will require that all applicants list their laptops, desktops, servers, computers, tablets and mobile phones, with details of the make and operating system. However, regarding firewalls and routers, the applicant will only be asked to list the make and model, but not the specific version of the firmware. By asking for the make and model of these devices, the Assessor will be able to determine if the devices are still receiving security updates to the firmware.
2. Asset management is important in Cyber Essentials
Similarly to backing up data, asset management isn’t a specific Cyber Essentials control, but it is a highly recommended core security function. By including this subject in the Cyber Essentials requirements, the importance of good asset management is being emphasised.
Why ?
The requirements clarify that asset management doesn’t mean making lists or databases that are never used, it means creating, establishing and maintaining authoritative and accurate information about your assets that enables both day-to-day operations and efficient decision making when you need it. Security experts often refer to asset management as a fundamental cyber hygiene practice that can help an organisation meet all of the Cyber Essentials’ five controls. Many major security incidents are caused by organisations having assets which are still connected to the network when that organisation is not aware the asset is still active. Effective asset management will help track and control devices as they’re introduced into your business.
The NCSC has comprehensive guidance for organisations on asset management.
3. A link to the NCSC’s BYOD guidance added for information
For further information and advice on the use of BYOD, please see the NCSC’s guidance.
4. Clarification on including third-party devices
All end user devices that your organisation owns and that are loaned to a third party must be included in the assessment scope. A new table is included for clarity on this subject
For devices not owned by your organisation, the table below explains what is in and out of scope: (use table from the requirements doc as the table should include crosses and ticks)
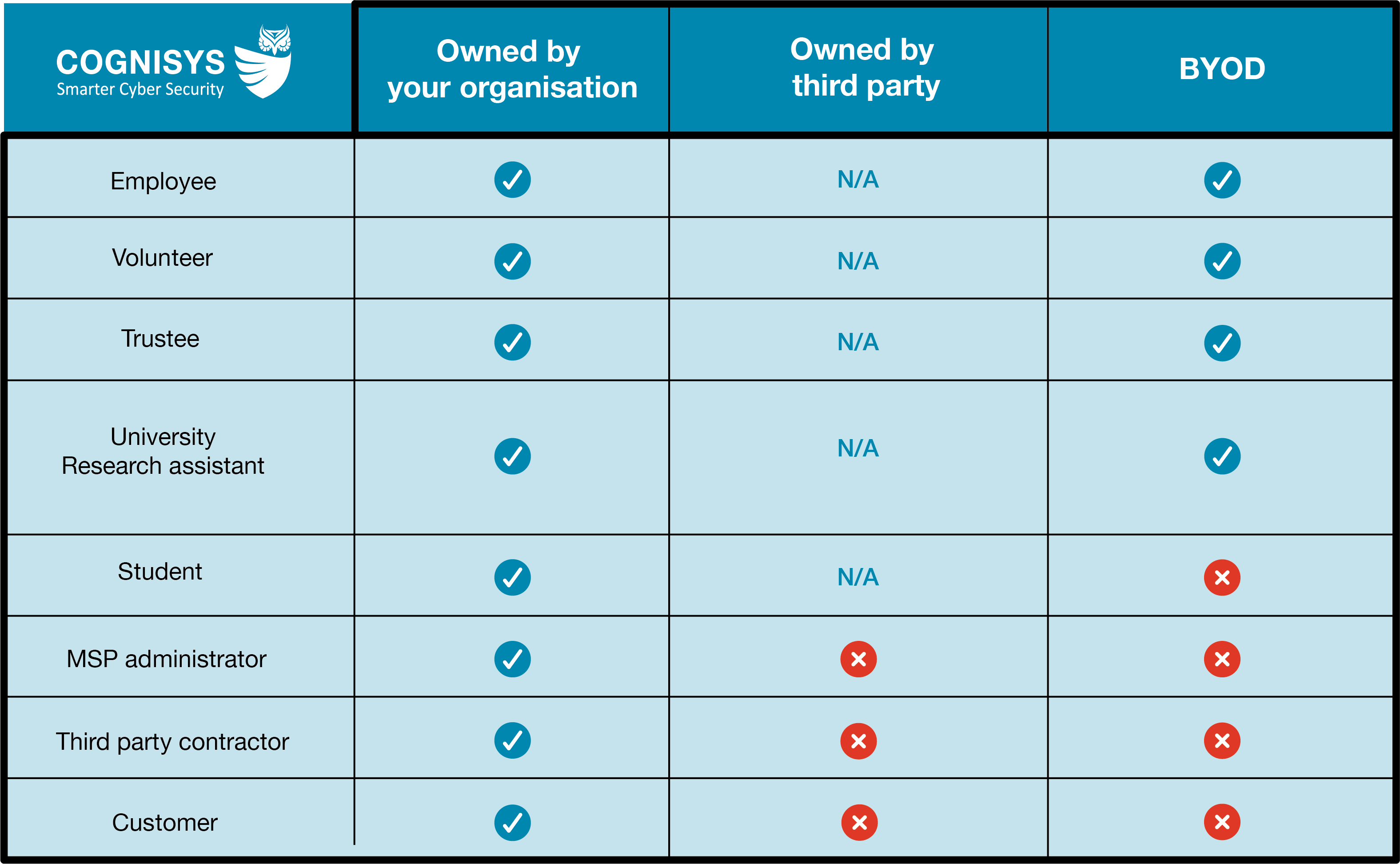
Why?
The new table gives clarity on which third party devices are in scope for Cyber Essentials. It aims to answer the common questions about consultants, volunteers, and the much disputed, student devices. When the third-party device has a green tick, it is in scope and the applicant organisation needs to demonstrate that they can apply the required controls via a combination of technical and written policy. For example, if an in scope third party BYOD connects to an organisational Office 365, the organisation can create a conditional access policy that says if the device doesn’t have a supported operating system, it won’t connect til the operating system is updated.
The devices of students that are not owned by the applicant organisation are not and have never been in scope.
5. ‘Device unlocking’ section has been updated to reflect that some configurations can’t be altered because of vendor restrictions
- When the vendor doesn’t allow you to configure the above, use the vendor’s default setting
Why?
Sometimes, an applicant might be using a device where there are no options to change the configuration to meet the Cyber Essentials requirements. One example of this is locking the device after 10 failed sign-in attempts. Samsung, possibly the largest provider of smartphones in the world, have set their minimum sign-in attempts at 15, with no option to alter this number. So, in this instance, Cyber Essentials would require that the applicant goes with the minimum number sign-in attempts allowed by the device before locking.
6. An updated ‘Malware protection’ section
You must make sure that a malware protection mechanism is active on all devices in scope. For each device, you must use at least one of the options listed below. In most modern products, these options are built in to the software supplied. Alternatively, you can purchase products from a third-party provider. In all cases the software must be active, kept up to date in accordance with the vendors instructions, and configured to work as detailed below:
Anti-malware software (option for inscope devices running Windows or MacOS, including servers, desktop computers, and laptop computers)
If you use anti-malware software to protect your device, it must be configured to:
- Be updated in line with vendor recommendations
- Prevent malware from running
- Prevent the execution of malicious code
- Prevent connections to malicious websites over the internet
Application allow listing (option for all in scope devices)
Only approved applications, restricted by code signing, are allowed to execute on devices. You must:
- Actively approve such applications before deploying them to devices
- Maintain a current list of approved applications, users must not be able to install any application that is unsigned or has an invalid signature
Why the change?
Questions have been raised about the efficacy of some of the controls to defend against malware. Requirements have been updated with the latest knowledge, research and recommendations from vendors.
7. Information about how using a zero trust architecture affects Cyber Essentials
Network architecture is changing. More services are moving to the cloud, and the use of Software as a Service (SaaS) continues to grow.
At the same time, many organisations are embracing flexible working, which means lots of different device types may connect to your systems from many locations. It’s also increasingly common for organisations to share data with their partners and guest users, which requires more granular access control policies.
Zero trust architecture is designed to cope with these changing conditions by enabling an improved user experience for remote access and data sharing.
A zero-trust architecture is an approach to system design where inherent trust in the network is removed. Instead, the network is assumed hostile, and each access request is verified based on an access policy. Confidence in a request is achieved by building context, which relies on strong authentication, authorisation, device health, and the value of the data being accessed.
NCSC and IASME have considered the alignment of Cyber Essentials with the zero trust architecture models. We are confident that implementing the Cyber Essentials technical controls does not prevent you from using a zero-trust architecture as defined by the NCSC guidance.
8. The illustrative specification document for CE+ has been updated and is published on January 23rd.
The changes regarding malware protection affect how a CE+ Assessor carries out the malware protection tests. At the point of CE+ audit, the Assessor will discuss further if required.
9. A number of style and language changes have been made to make the document more readable
The requirements document has been updated in line with plain English and accessibility guidelines.
10. The technical controls have been reordered to align with the self-assessment question set
For consistency, the scheme requirements are now in the same order as the question set which is, firewalls, secure configuration, security update management, user access controls, and malware protection.
Overall, the Cyber Essentials requirements have been updated to provide more clarity and reflect changes in technology and security practices. These updates include defining the scope of software, emphasizing the importance of asset management, clarifying third-party device inclusion, and updating the malware protection section. Additionally, the new requirements address the growing trend of zero trust architecture and the use of SaaS. Overall, these changes aim to enhance the security of organizations and promote best practices in cybersecurity.
Get a copy of the lattes Cyber Essentials: Requirements for IT infrastructure v3.1 document here.
If you want to learn more and see how secure your organisation truly is, get in touch with our experts today.
And for more information regarding Cyber Essentials, take a look here.